Fractional Ownership in Real Estate vs. REITs: Exploring the Future of Property Investment
Real estate has long been a famous Investment Avenue, offering the potential for long-term growth and passive income. Traditionally, investing in real estate requires substantial capital and extensive management responsibilities. However, with the emergence of fractional ownership and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), individuals now have alternative options to participate in the real estate market. In this blog post, we will delve into fractional ownership and REITs, comparing their benefits and drawbacks and exploring how they shape the future of property investment.
Understanding Fractional Ownership:
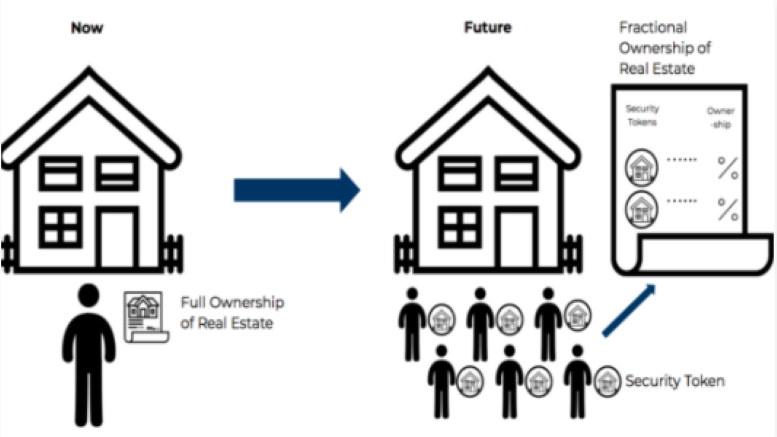
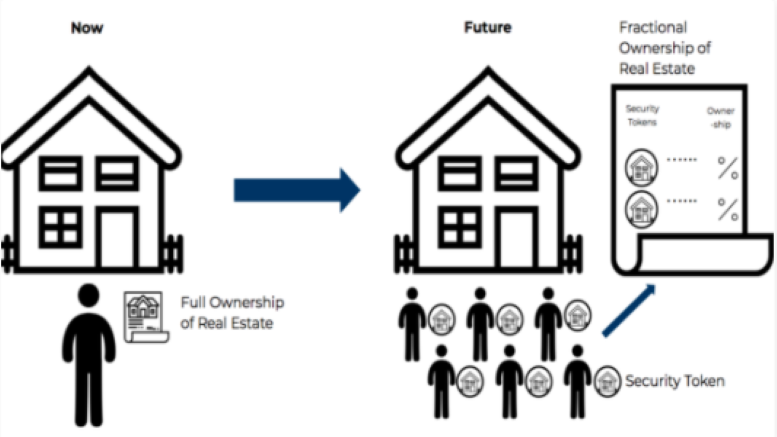
Fractional ownership, also known as crowdfunded real estate or property syndication, is an innovative investment model that enables multiple investors to pool their resources and collectively purchase a property. Investors acquire shares or units in the property, entitling them to a proportional share of the property’s income, appreciation, and potential tax benefits. This model allows individuals with smaller budgets to invest in high-value properties that would otherwise be financially out of reach.
One of the significant advantages of fractional ownership is the diversification it offers. Investors can spread their investments across various properties, mitigating risk and reducing exposure to the volatility of a single property. Additionally, fractional ownership platforms provide transparency and ease of access, allowing investors to monitor their investments, receive regular updates, and make informed decisions.
Exploring REITs:
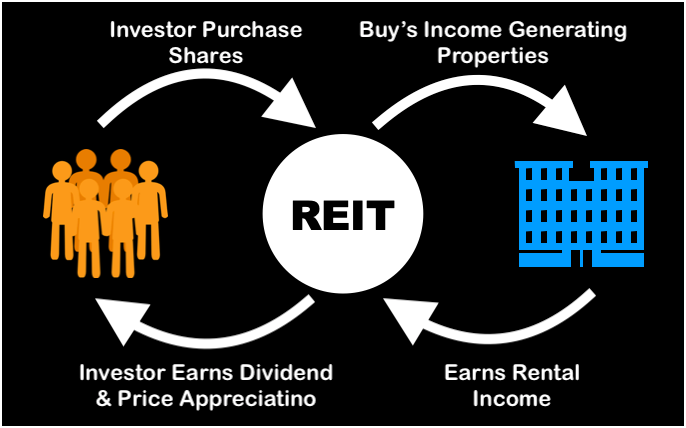
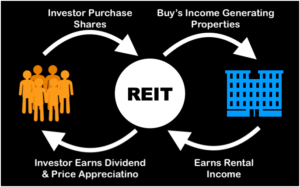
REITs are investment vehicles that pool funds from multiple investors to invest in a portfolio of income-generating properties. Unlike fractional ownership, REITs are publicly traded on stock exchanges, providing investors with liquidity and the ability to buy or sell shares quickly. They offer a simple and convenient way to invest in real estate without direct property ownership.
One of the critical advantages of REITs is the potential for passive income. REITs distribute a significant portion of their rental income as dividends to shareholders, offering investors a regular income stream. Additionally, investing in REITs provides diversification across a wide range of properties and geographical locations, reducing risk compared to investing in a single property. As of November 2022, India has three REITs listed on the stock market. These include Embassy Office Parks REIT, Mindspace Business Parks REIT, and Brookfield India Real Estate Trust REIT.
Comparing Fractional Ownership and REITs:
When considering fractional ownership and REITs, evaluating their respective benefits and drawbacks is essential. Fractional ownership allows investors to own a specific property directly, giving them more control over their investment decisions. It offers potential tax advantages, such as depreciation deductions, which may vary depending on the jurisdiction. However, fractional ownership typically requires a longer-term commitment, as the property may take time to sell or liquidate.
On the other hand, REITs provide investors with liquidity and flexibility. Shares can be bought or sold on stock exchanges, allowing investors to adjust their portfolios quickly. REITs also offer professional management, relieving investors of the responsibilities associated with property maintenance and tenant management. However, as publicly traded entities, REITs are subject to market fluctuations, and broader economic factors may influence their value.
The Future of Property Investment:
Fractional ownership and REITs have gained significant traction in real estate investment. They cater to different investor preferences and risk appetites, offering alternatives to traditional property ownership. We can expect further innovation and refinement in these investment models as technology advances. In the future, we may witness the integration of blockchain technology, allowing for increased transparency, security, and fractionalization of real estate assets. This could further enhance the accessibility and efficiency of fractional ownership. Similarly, REITs may adopt more specialized strategies, such as focusing on specific property types or sustainable investments, catering to the evolving demands of investors.